Radon and Lung Cancer: What West Michigan Homeowners Need to Know
Radon is the #2 cause of lung cancer in the U.S. Learn how exposure raises risk—and how West Michigan homeowners can protect their families.
Schedule a Radon Test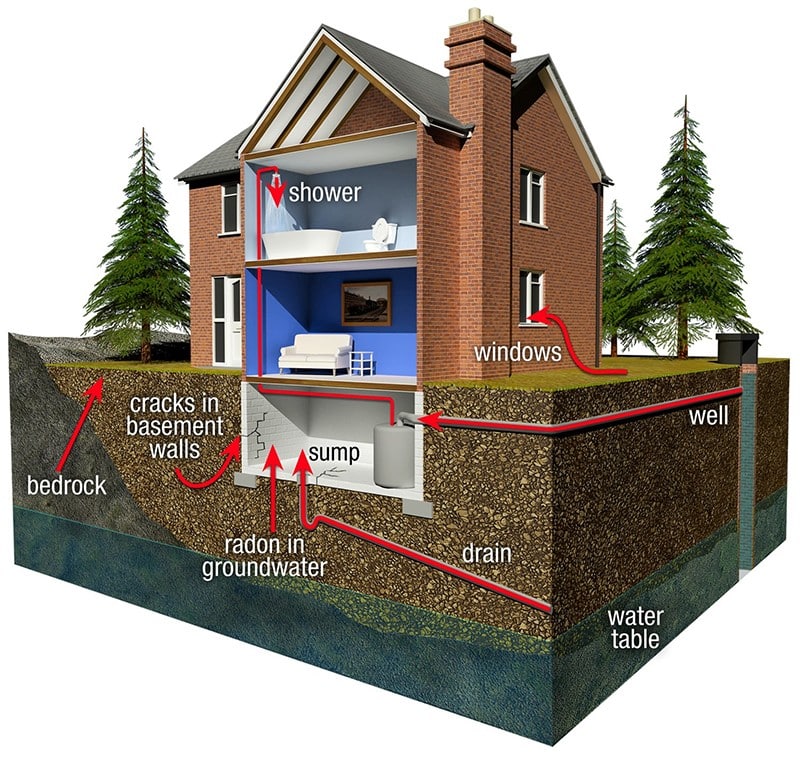
What is Radon?
Radon is a naturally occurring radioactive gas released from the breakdown of uranium in soil and rock. Outdoors it disperses harmlessly, but indoors it can build up—especially in basements and slab-on-grade homes—raising the risk of radon-related lung cancer.
- Invisible and odorless—only testing can detect it.
- Measured in picocuries per liter (pCi/L); EPA action level is 4.0 pCi/L.
- Common in West Michigan due to local geology and housing styles.
Does Radon Cause Lung Cancer?
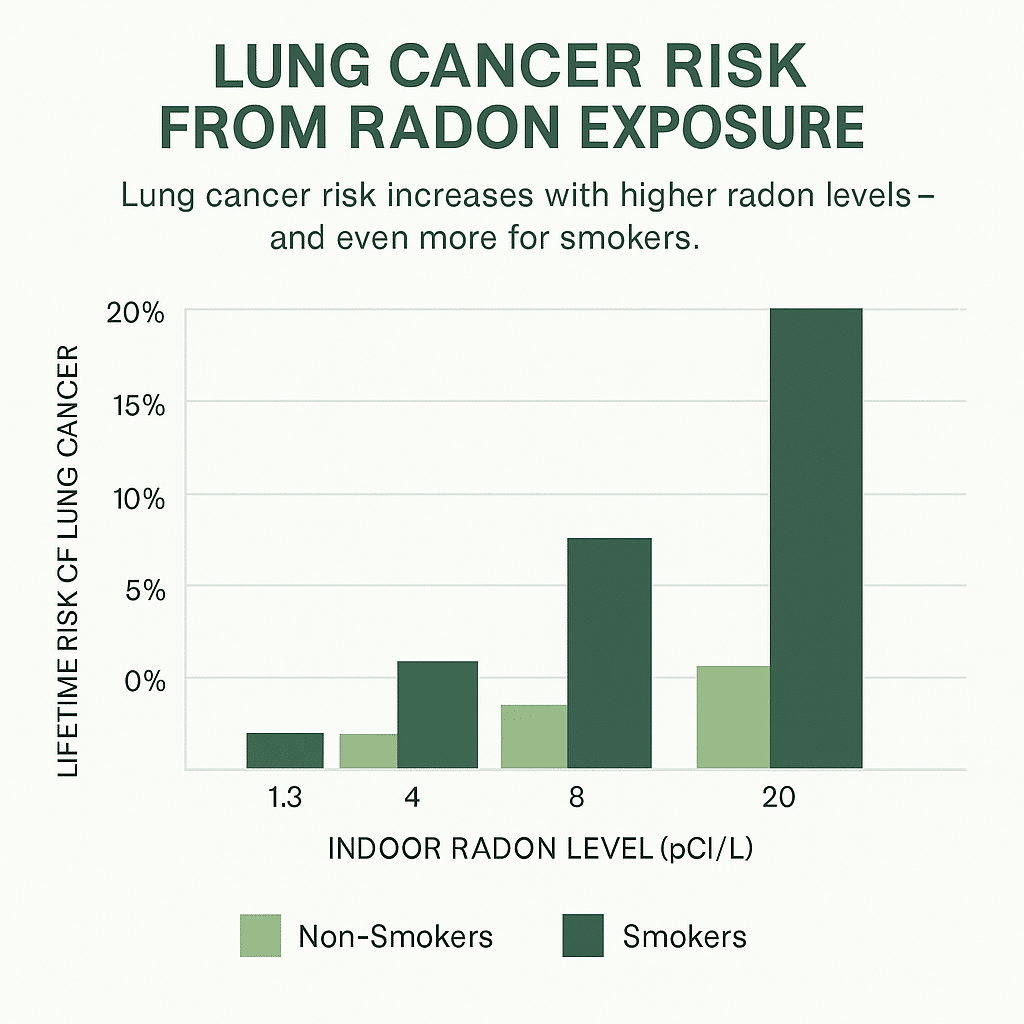
Yes. When you breathe radon gas, radioactive decay particles (radon progeny) can lodge in the lungs. Over time, this radiation damages lung tissue and increases the risk of lung cancer. Radon is the #2 cause of lung cancer in the U.S., and the risk is even higher for smokers.
How Radon Exposure Leads to Cancer
- Microscopic particles: Radon decay products attach to dust and are inhaled.
- DNA damage: Alpha radiation can damage cells in the lung lining.
- Compounding risk: Smoking + radon exposure multiplies lung cancer risk.
Radon Lung Cancer Risk Factors
Certain conditions and habits can significantly increase the chances of developing lung cancer from radon exposure. Understanding these factors helps you take steps to reduce your risk.
Long-Term Exposure
The longer you’re exposed to elevated radon levels, the greater your lifetime risk of developing lung cancer.
High Radon Levels at Home
Homes in West Michigan often exceed the EPA action level of 4.0 pCi/L, especially in basements and lower floors.
Smoking Combined with Radon
Smokers face a much higher risk when exposed to radon gas, due to the combined effects on lung tissue.
Preventing Radon-Related Lung Cancer
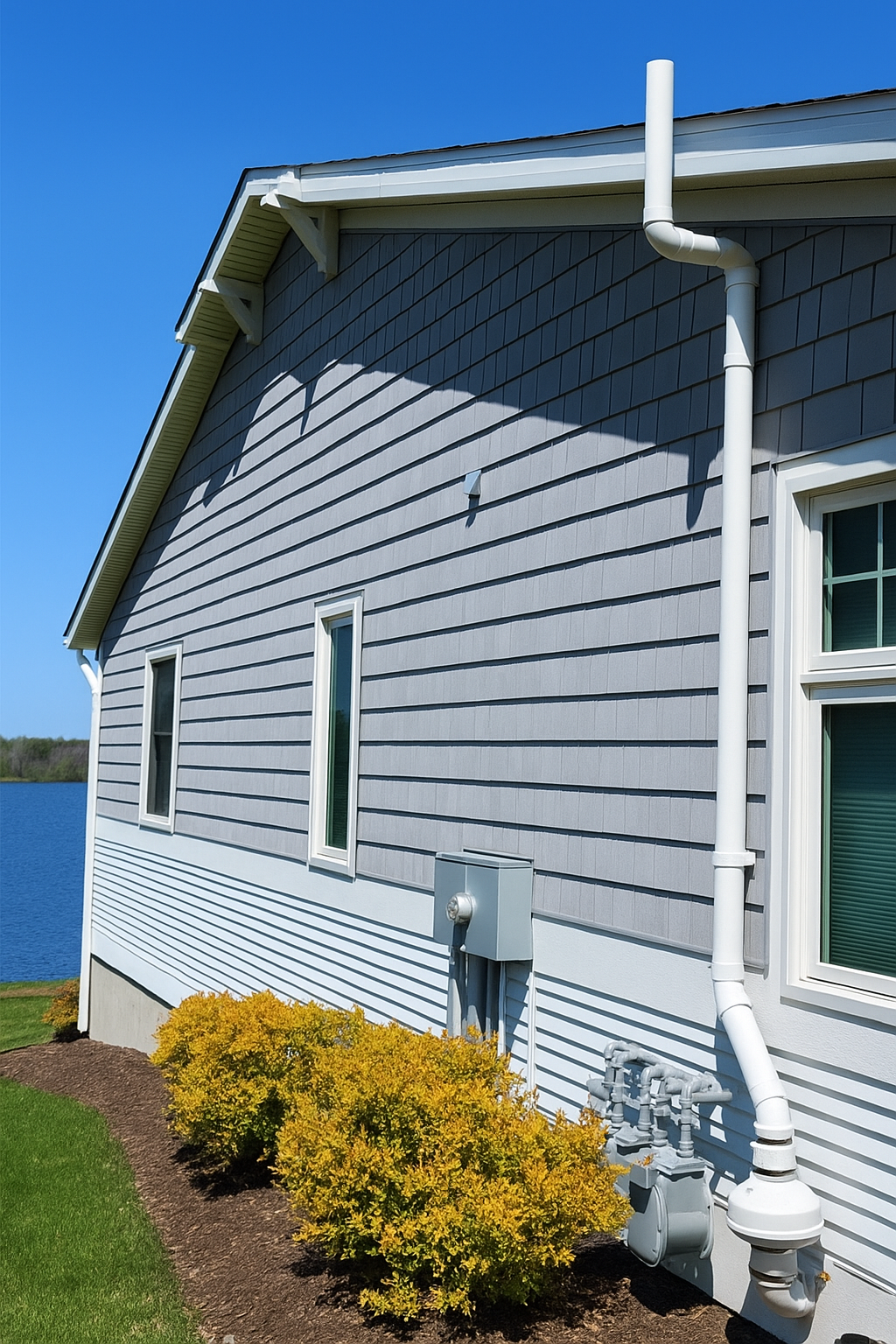
Testing is the only way to know your home’s radon level. If readings are high, a properly designed mitigation system vents radon outdoors before it reaches your living spaces—dramatically reducing your family’s risk.
- Test continuously or at least every 2 years or after renovations and foundation work.
- Install a certified mitigation system if levels ≥ 4.0 pCi/L (EPA action level).
- Monitor continuously to verify performance through seasons.

Radon & Lung Cancer FAQs
Quick answers to the most common questions about radon exposure and lung cancer risk in West Michigan.
Can radon cause lung cancer?
Yes. Radon is the #2 cause of lung cancer in the U.S. after smoking. Its radioactive decay particles can damage lung tissue when inhaled over time.
How long does radon exposure take to cause lung cancer?
Risk builds with long-term exposure and higher concentrations. Years of elevated levels significantly raise lifetime risk, especially for smokers.
What are the symptoms of radon exposure?
Radon itself has no immediate symptoms. Health effects show up as lung cancer signs (persistent cough, chest pain) that often appear late—another reason testing is critical.
Does radon cause lung cancer in non-smokers?
Yes. Many radon-related lung cancer deaths occur in non-smokers. Combined exposure with smoking multiplies the risk.
What radon level is considered unsafe?
The EPA’s action level is 4.0 pCi/L. Levels between 2.0 and 3.9 pCi/L still warrant mitigation consideration, especially for sensitive households.
How do I reduce my radon levels?
A licensed installer can add a sub-slab depressurization (ASD) system that vents radon above the roofline. Continuous monitoring verifies performance year-round.
How long does radon remediation take?
A licensed installer can add a sub-slab depressurization (ASD) system that vents radon above the roofline. Continuous monitoring verifies performance year-round.How do I reduce my radon levels?
Lets Get in Touch
Contact SM Radon today for your free consultation.
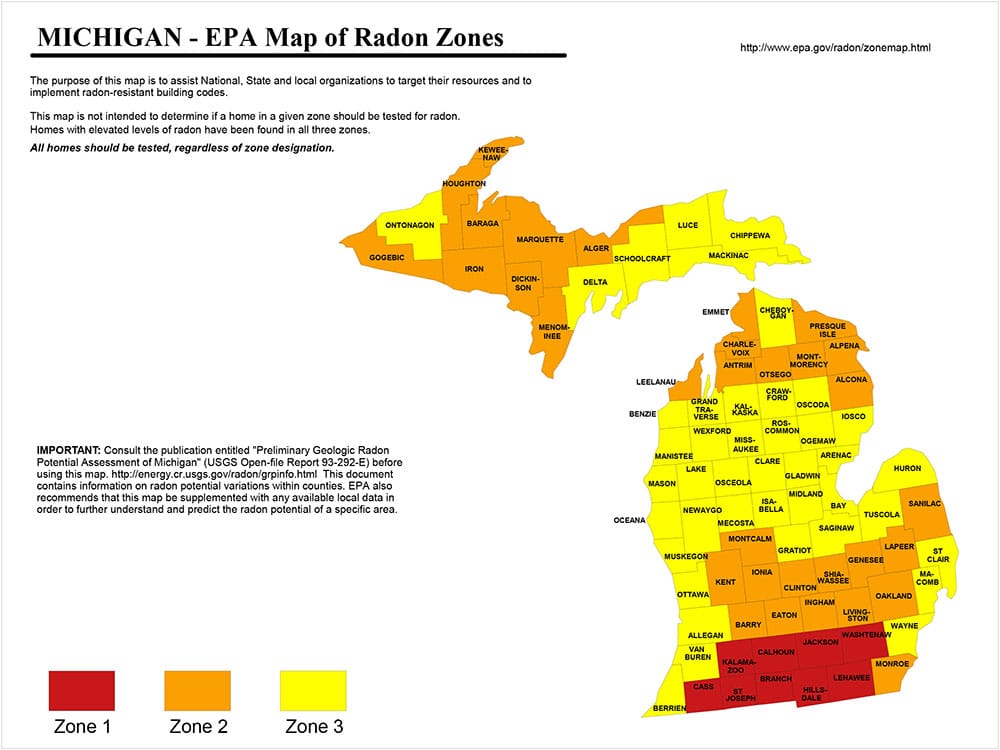
Radon Risk in West Michigan — Take Action Today
Many counties in West Michigan—including Kent, Ottawa, Muskegon, and Ionia—report elevated indoor radon levels. Testing is the only way to know your home’s level, and mitigation can reduce radon dramatically within a day.
- Fast scheduling and certified results
- EPA-compliant mitigation systems
- Local expertise across Grand Rapids & surrounding areas